Microkinetics
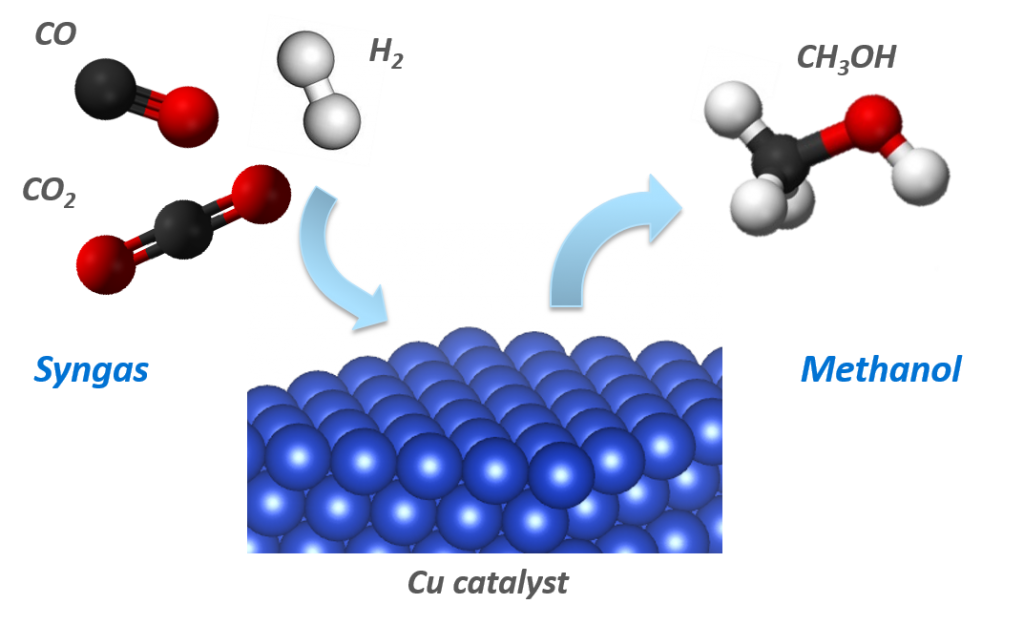 Microkinetic modeling in catalytic reaction systems: Unlike the conventional kinetic models (e.g., power-law model, Langmuir-Hinshelwood-Hougen-Watson (LHHW) model), a microkinetic model does not assume the rate-limiting steps or equilibrated steps.
Microkinetic modeling in catalytic reaction systems: Unlike the conventional kinetic models (e.g., power-law model, Langmuir-Hinshelwood-Hougen-Watson (LHHW) model), a microkinetic model does not assume the rate-limiting steps or equilibrated steps.
Possible elementary steps of the overall reactions are listed, and site balance equations for the surface intermediates are solved.
By a microkinetic model, the reaction mechanisms are elucidated; the dominant pathway, the rate-limiting step, and the most abundant surface intermediate are investigated. In addition, case studies on effects of operating conditions are conducted.
In summary, microkinetic modeling covers the chemical reaction and reactor engineering with the detailed reaction mechanisms.



In order to calculate the site balance equations, the kinetic parameters are derived on the basis of the computational chemistry (e.g., DFT, MP2) and the parameter estimation using the genetic algorithm (GA).

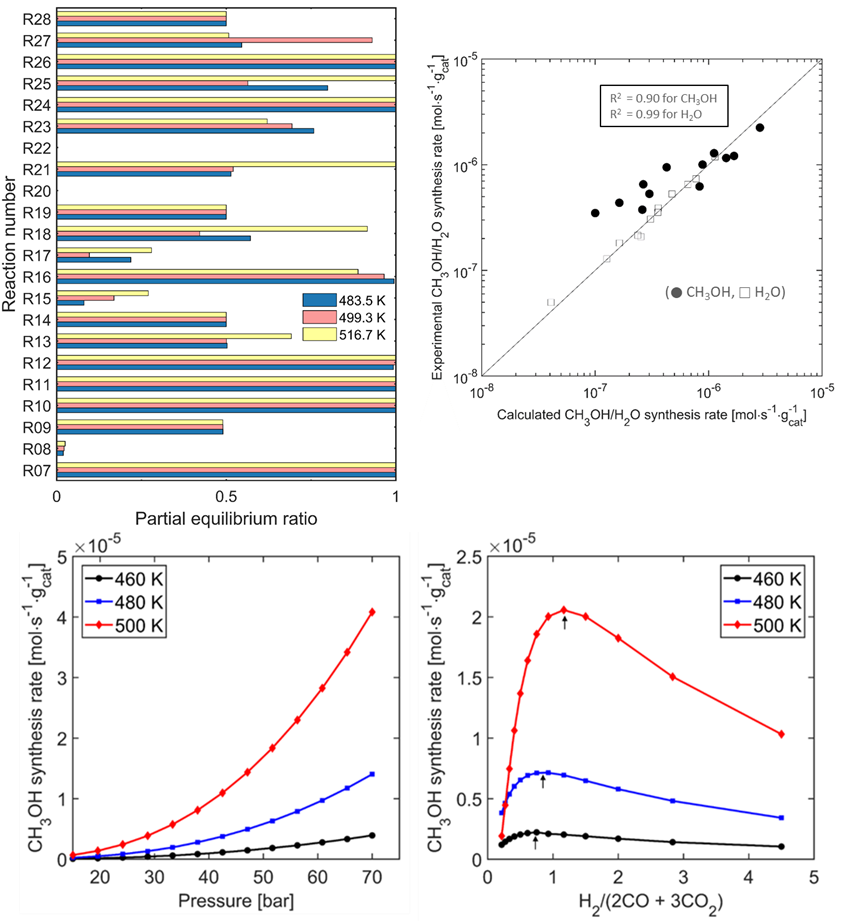
Reference: Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 20, 8663-8673.